
Monocyte-Chemoattractant Protein-1 Levels in Human Atherosclerotic Lesions Associate With Plaque Vulnerability | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Proteolytic Activation of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 by Plasmin Underlies Excitotoxic Neurodegeneration in Mice | Journal of Neuroscience

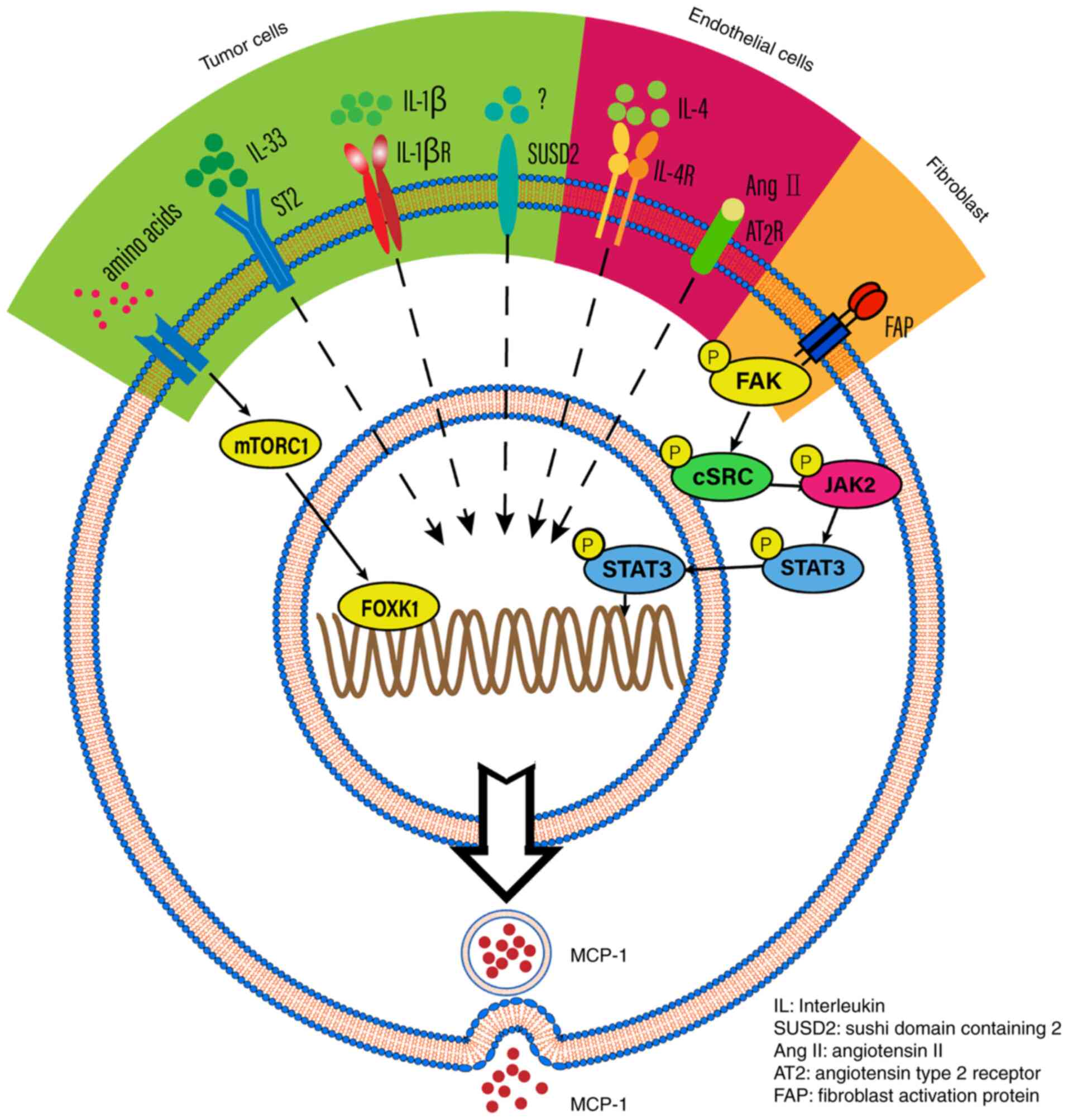
The chemokine MCP-1 (CCL2) in the host interaction with cancer: a foe or ally? | Cellular & Molecular Immunology
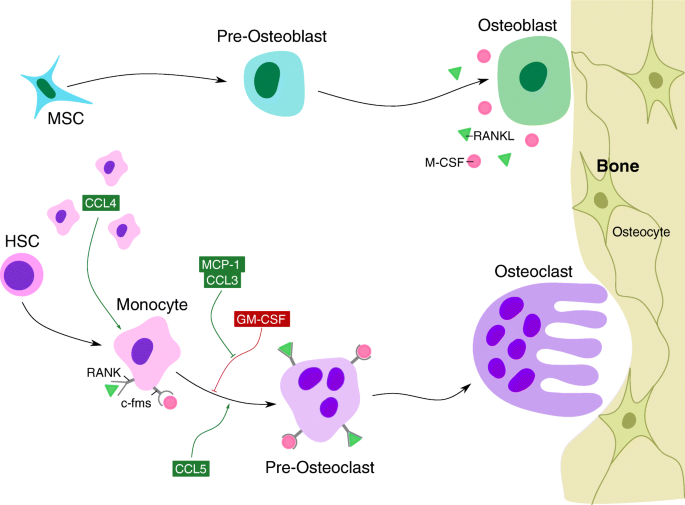
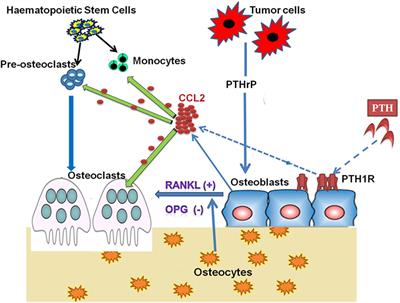
Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2) Drives Activation of Bone Remodelling and Skeletal Metastasis | Current Osteoporosis Reports

Role of MCP-1 and CCR2 in ethanol-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the developing brain | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text

Dichotomous Roles of Smooth Muscle Cell–Derived MCP1 (Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1) in Development of Atherosclerosis | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) mediated decrease in CYP3A4... | Download Scientific Diagram

Model of proposed mechanism for monocyte arresting. MCP-1/CC12 binds to... | Download Scientific Diagram
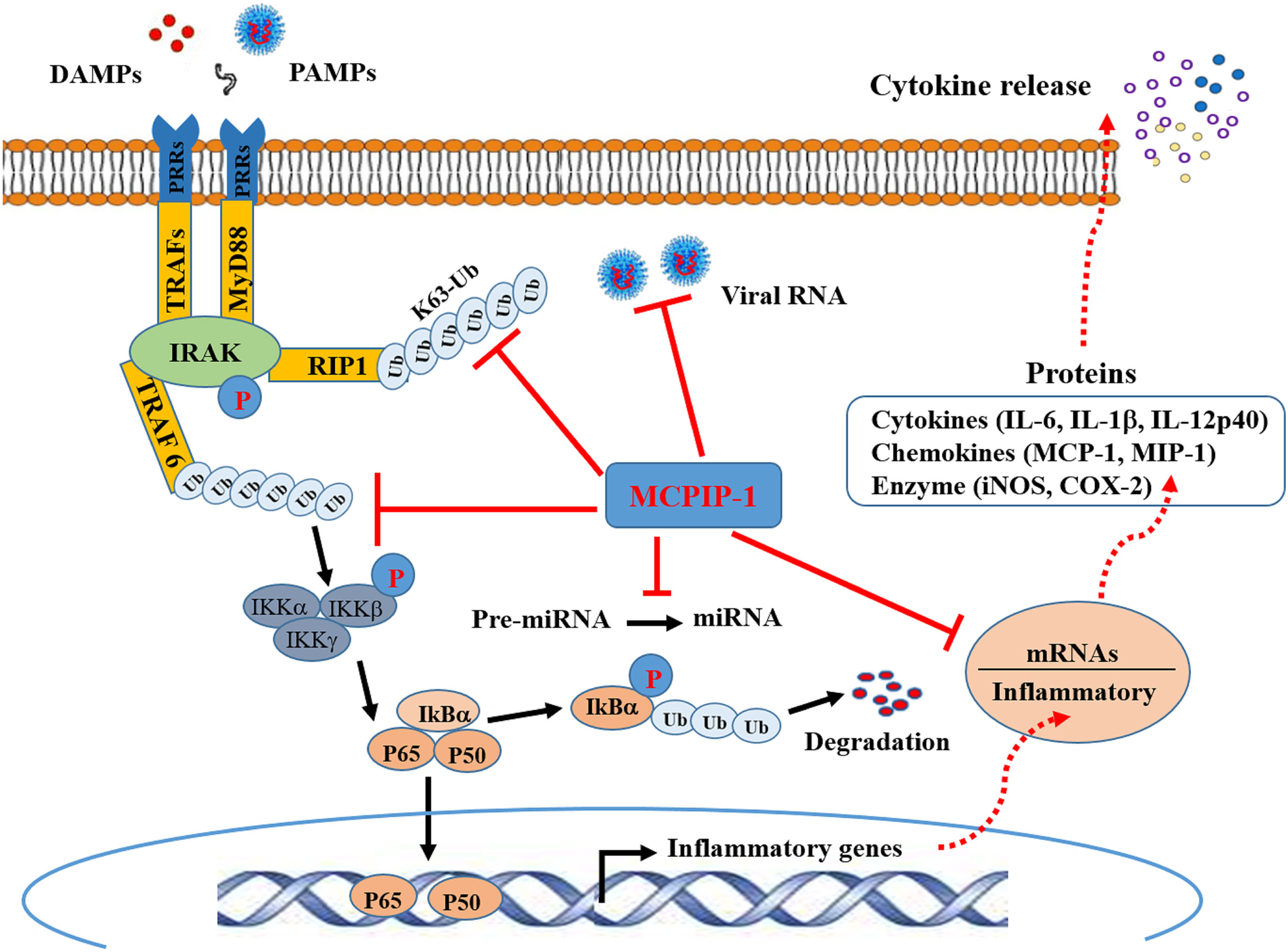
Frontiers | Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-Induced Protein 1 (MCPIP-1): A Key Player of Host Defense and Immune Regulation

MCP-1/CCL2 Protein Overview: Sequence, Structure, Function and Protein Interaction | Sino Biological
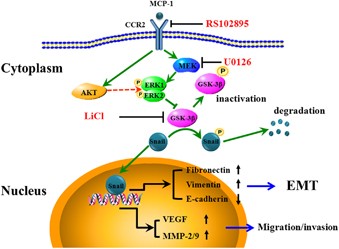
MCP-1-induced ERK/GSK-3β/Snail signaling facilitates the epithelial–mesenchymal transition and promotes the migration of MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells | Cellular & Molecular Immunology

The chemokine MCP-1 (CCL2) in the host interaction with cancer: a foe or ally? | Cellular & Molecular Immunology
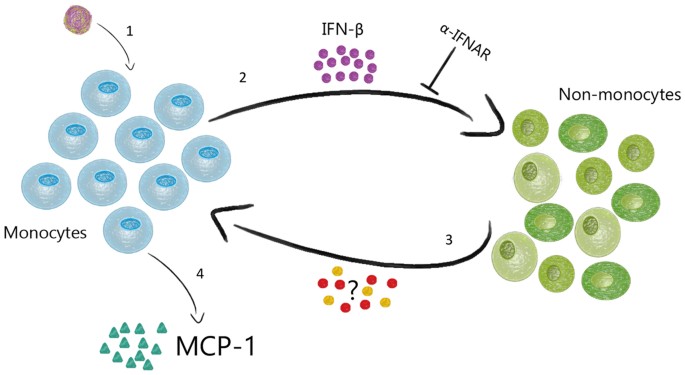
Mechanism and role of MCP-1 upregulation upon chikungunya virus infection in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells | Scientific Reports
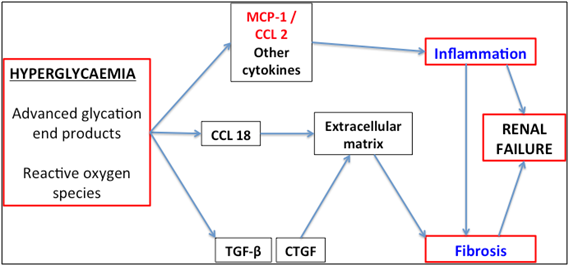
Review Article - MCP-1: A Potential Target for Diabetic Microvascular Complications? - MedCrave online





![PDF] Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in luteolysis. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in luteolysis. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/970a1fe0301d593ca04772623e90427e25780744/3-Figure1-1.png)




